Cyber threats: a new issue for space security
Abstract
For a long time, reflections on space security have focused on attacks of a kinetic nature or of electromagnetic origin. With the expansion of cyberspace, the space industry has had to consider new threats and new types of actors. In a context of growing concern among space powers about the risks of armed militarization of space, this note provides a strategic and legal overview of the main issues linked to cyberthreats targeting space systems.
About the Author
Benoît Wagner is a doctoral student at the Alexandre Koyré center of the EHESS under the supervision of Isabelle Sourbès-Verger and at the LORIA (Lorraine computer science laboratory and its applications) under the supervision of Didier Fass. His research, funded by the Agence Innovation Défense, focuses on the strategic and legal aspects of the defense of French space systems against cyberthreats.


In politics, the community of hatred almost always forms the basis of friendships.

"Is there, strictly speaking, a reasonable possibility of "control" from the moment one succumbs to the temptation to consider nuclear weapons, whatever their characteristics, as means of deterrence other than existential ? "


Technology-capability analysis

The silent masters of the oceans: the strategic and non-proliferation implications of nuclear-powered submarines in Australia and Brazil
At the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) General Conference in 2022, Director General Rafael Grossi emphasizes that “the world of nuclear proliferation and safeguards is changing,” and that this change creates important technical and political challenges. The announcement of the AUKUS agreement and the progress of Brazil’s nuclear-powered submarine program reflect regional geopolitical realignments. Internationally, the IAEA safeguards system is challenged by these developments insofar as they entail risks of nuclear proliferation. How does the acquisition of nuclear-powered submarines impact both the regional and international strategic balance and nuclear non-proliferation norms? The purpose of this research note is to analyze the geopolitical motivations of nuclear-powered submarine programs in Australia and Brazil and their implications for nonproliferation instruments.
𝐉𝐚𝐧𝐮𝐚𝐫𝐲 𝟐𝟎𝟐𝟑
The affirmation of the U.S. space nuclear technology strategy
Since 2017, U.S. interest in space-based nuclear power applications appears renewed. In a context of growing international competition, these applications are even receiving increasingly structured political support. The objective of this note is to examine these developments in order to put into perspective the issues that accompany them. Although primarily intended for interplanetary exploration (surface energy supply and high-performance propulsion), space nuclear technologies remain dual.
The Nuclear Sea-Launched Cruise Missile (SLCM-N): Implication for U.S. nuclear strategy and arms control
In May 2021, soon after taking office, the Biden administration confirmed the decision to fund the NucleaSea-launched Cruise Missile (SLCM-N), one of the most controversial programs of Donald Trump’s term. The decision was received with surprise by some analysts: Joseph Biden had argued against this new weapon during his campaign. Finally, after considerable discussion within the government and the armed forces, the Democratic administration appears to have reconsidered its decision and canceled the SLCM-N program.
À lire également

The affirmation of the U.S. space nuclear technology strategy
Since 2017, U.S. interest in space-based nuclear power applications appears renewed. In a context of growing international competition, these applications are even receiving increasingly structured political support. The objective of this note is to examine these developments in order to put into perspective the issues that accompany them. Although primarily intended for interplanetary exploration (surface energy supply and high-performance propulsion), space nuclear technologies remain dual.
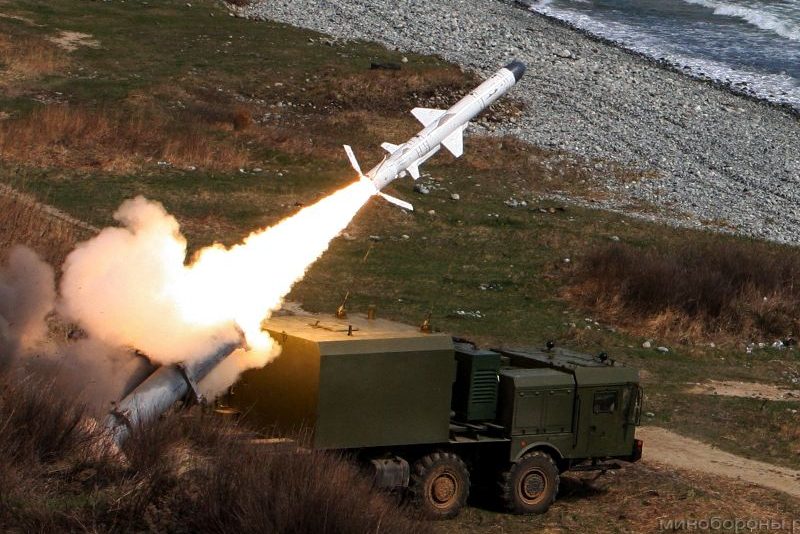

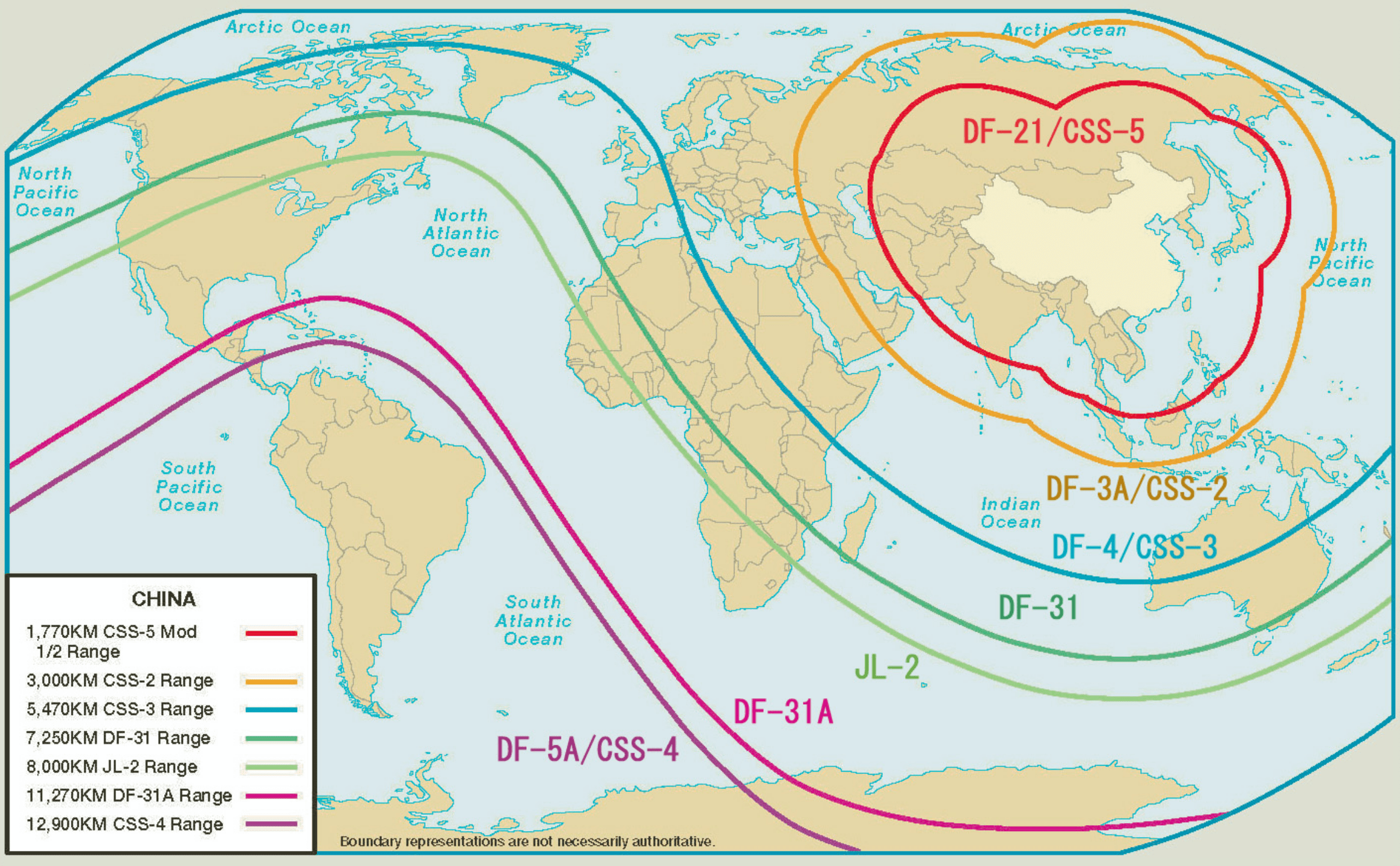
The missile standoff: ballistic considerations of the war in Ukraine
On February 24, 2022, after a few months of strategic uncertainty on the Russian-Ukrainian borders, Russian President Vladimir Putin launched a military offensive in Ukraine. This attack confirmed the aggressive intentions of Russia, which had amassed military forces on the Ukrainian border since December 2021. It also confirmed the concretization of Russia’s efforts to remain a major power in the ballistic field.

The legal consequences of the nuclearisation of Belarus
Belarus, which borders Ukraine and Poland, has just changed its constitution to become a nuclear state. The referendum of 27 February 2022 approved the proposed constitutional amendments by more than 65%, thus ending the previous status of the Belarusian territory, which had been designated as a neutral and non-nuclear zone. The amended version should also include an article excluding military aggression from Belarusian territory, which would legally allow for the deployment of nuclear weapons by its ally, Russia.


