Alternatives to the aircraft carrier: an analysis of the French strategic debate
Abstract
Since the end of the Second World War, the status of capital ship of the aircraft carrier has been a consensus. However, the criticisms against him seem to be on the increase today. These are based on geostrategic, techno-capability and / or economic considerations. Although such accusations in no way slow down the renewed global interest in the acquisition of naval air platforms, capability introspection must be engaged: does the aircraft carrier still embody the flagship of a fleet? Are alternative and more appropriate solutions possible? Concerned by this debate because of its national flagship – the Charles de Gaulle – and at the time of choosing its successor, France must lead this reflection. Is the model of the large aircraft carrier still of interest for the French Navy or can it count on alternative solutions? If so, are we in the process of witnessing the establishment of a new naval capability system in the coming decades, sanctioning the emergence of a new capital ship?
About the Author
Pierre Vallée holds a degree in History / Political Science (ICR - Rennes) and a Master II in Relations international, International Security and Defense course (Jean Moulin University - Lyon III). In the framework of of his final thesis (2019), he was interested in the evolutions and the future of naval power French. Since the end of his Masters, he has been a researcher at the Institute of Strategy and Defense of Lyon.
Technology-capability analysis

The silent masters of the oceans: the strategic and non-proliferation implications of nuclear-powered submarines in Australia and Brazil
At the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) General Conference in 2022, Director General Rafael Grossi emphasizes that “the world of nuclear proliferation and safeguards is changing,” and that this change creates important technical and political challenges. The announcement of the AUKUS agreement and the progress of Brazil’s nuclear-powered submarine program reflect regional geopolitical realignments. Internationally, the IAEA safeguards system is challenged by these developments insofar as they entail risks of nuclear proliferation. How does the acquisition of nuclear-powered submarines impact both the regional and international strategic balance and nuclear non-proliferation norms? The purpose of this research note is to analyze the geopolitical motivations of nuclear-powered submarine programs in Australia and Brazil and their implications for nonproliferation instruments.
𝐉𝐚𝐧𝐮𝐚𝐫𝐲 𝟐𝟎𝟐𝟑
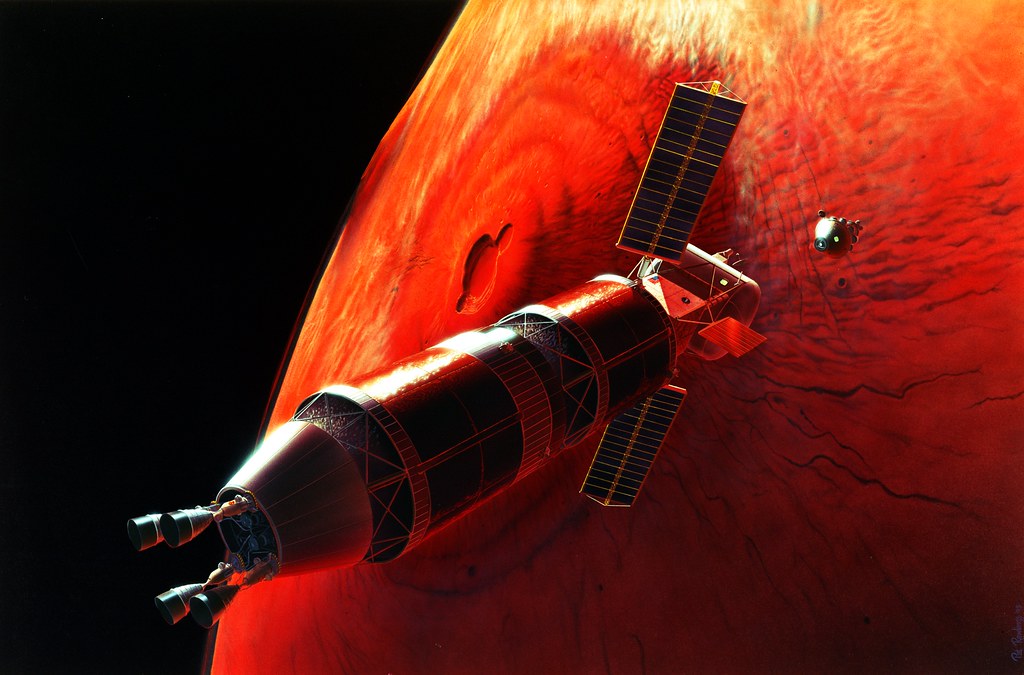
The affirmation of the U.S. space nuclear technology strategy
Since 2017, U.S. interest in space-based nuclear power applications appears renewed. In a context of growing international competition, these applications are even receiving increasingly structured political support. The objective of this note is to examine these developments in order to put into perspective the issues that accompany them. Although primarily intended for interplanetary exploration (surface energy supply and high-performance propulsion), space nuclear technologies remain dual.
The Nuclear Sea-Launched Cruise Missile (SLCM-N): Implication for U.S. nuclear strategy and arms control
In May 2021, soon after taking office, the Biden administration confirmed the decision to fund the NucleaSea-launched Cruise Missile (SLCM-N), one of the most controversial programs of Donald Trump’s term. The decision was received with surprise by some analysts: Joseph Biden had argued against this new weapon during his campaign. Finally, after considerable discussion within the government and the armed forces, the Democratic administration appears to have reconsidered its decision and canceled the SLCM-N program.
À lire également

The silent masters of the oceans: the strategic and non-proliferation implications of nuclear-powered submarines in Australia and Brazil
At the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) General Conference in 2022, Director General Rafael Grossi emphasizes that “the world of nuclear proliferation and safeguards is changing,” and that this change creates important technical and political challenges. The announcement of the AUKUS agreement and the progress of Brazil’s nuclear-powered submarine program reflect regional geopolitical realignments. Internationally, the IAEA safeguards system is challenged by these developments insofar as they entail risks of nuclear proliferation. How does the acquisition of nuclear-powered submarines impact both the regional and international strategic balance and nuclear non-proliferation norms? The purpose of this research note is to analyze the geopolitical motivations of nuclear-powered submarine programs in Australia and Brazil and their implications for nonproliferation instruments.
𝐉𝐚𝐧𝐮𝐚𝐫𝐲 𝟐𝟎𝟐𝟑

High strategic capabilities and defensive military assistance in the Ukraine war: the double threshold dilemma
One of the major elements of the Russian-Ukrainian confrontation is of course its potential nuclear nature. This dimension encourages the Biden administration not to let the war in Ukraine degenerate into a major conflict that would directly oppose Americans and Russians. This limit makes the problem of Western co-belligerence a key element in the political-military equation of the conflict. Taking this context into account, this note relates the tactical-operational “threshold” related to this arms supply to a second threshold of a politico-strategic nature, which in turn is influenced by the phenomenon of the interconnection of high strategic capabilities, and which opens up the delicate concept of multi-domain deterrence.
𝐉𝐚𝐧𝐮𝐚𝐫𝐲 𝟐𝟎𝟐𝟑



